There are numerous Two-dimensional NMR (2D NMR) techniques that can give structural information about your molecule. Each experiment looks at the molecule in a slightly different scenario to give information about bond connectivity or spatial arrangement of a molecule. The data for 2D NMRs is plotted on two frequency axes with the central area showing correlation signals.
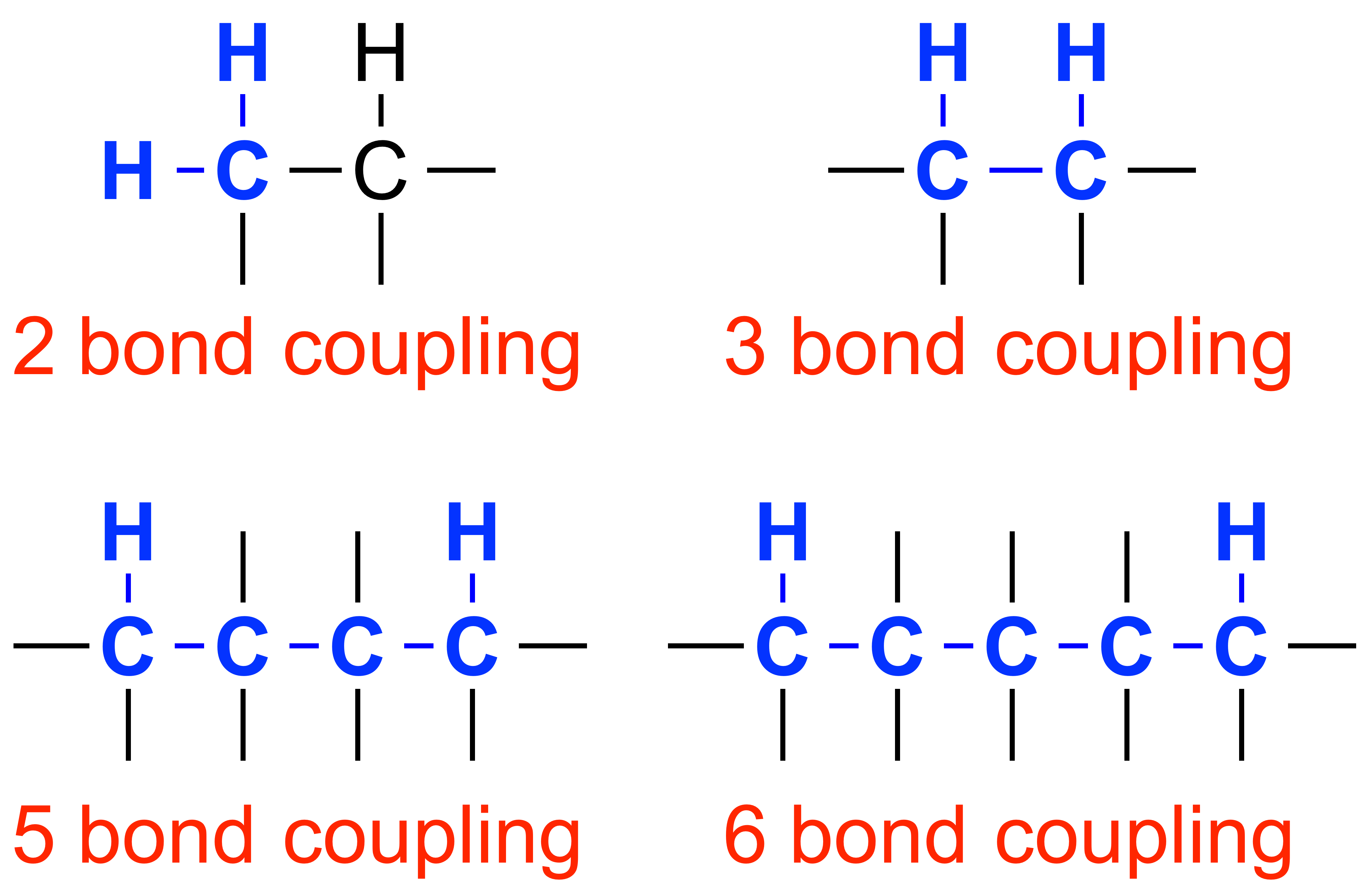
COSY: COrrelation SpectroscopY is a 2D spectroscopic technique used to view the connectivity of hydrogens through the bond. A cross peak arises when there is a correlation between signals on axis, indicating coupling between the hydrogens. COSY is used to view 2 to 3 bond couplings to assign proton environments for a molecule in a proton NMR. This technique is especially useful for differenitating multiple protons with similar functionality.
TOCSY: TOtal Correlation SpectroscopY, an experiment similar to COSY, can be useful in stereochemical assignment and to view 2 to 3 bond couplings, as well as couplings up to 5 to 6 bonds away. TOCSY especially useful for proton assignments on a ring.
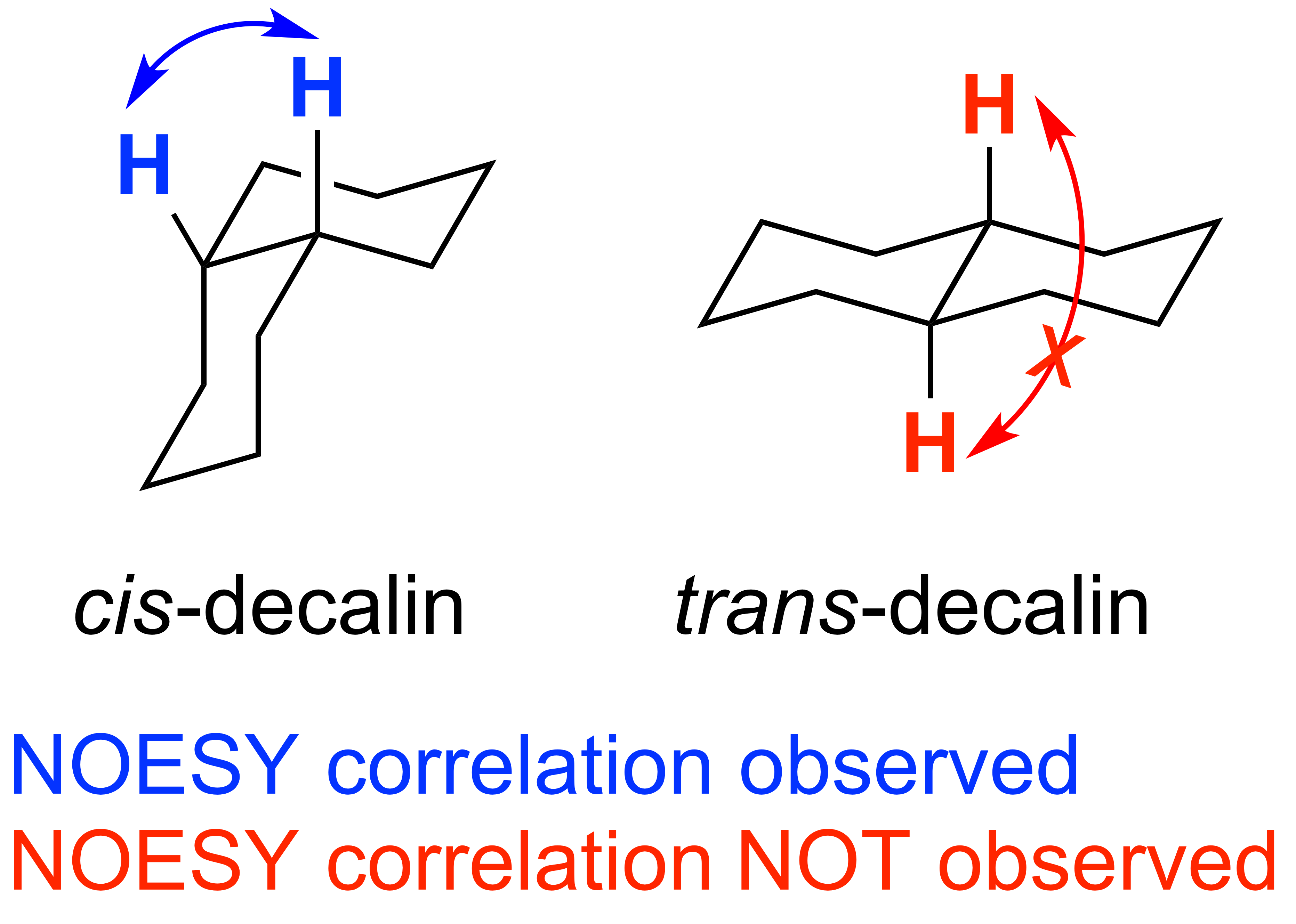
NOESY: Nuclear Overhauser Effect SpectroscopY is a spectroscopic technique used to view how hydrogen atoms are positioned in 3D space. Hydrogens will show a correlation if they are within 5 angstroms of each other. NOESY and ROESY are similar experiments, but NOESY is more appropriate on molecules with a low molecular weight (less than 1000 amu).
ROESY: Rotating Frame Overhauser Effect SpectroscopY, is another spectroscopic technique used to see hydrogens in 3D space but differs by shifting magnet equilbrium from the Z-axis to the X-axis. This difference in experimental parameters makes this a more appropriate for molecules with a high molecular weight (more than 1000 amu).

HMBC: Heternuclear Multiple-Bond Correlation spectroscopy, is a technique used to view hydrogen-carbon corrleations from 2-4 bonds. Direct 1 bond correlations are suppressed. HMBC is particular useful in assignments of conjugated systems.
HSQC: Heteronuclear Single-Quantum Correlation spectroscopy, similar to HMBC, is another technique used to view bond correlations between hydrogen and carbon. HSQC is particular useful in assignments of protons and carbon in a ring due to better sensitivity up to 5-6 bonds away.